Historical Price Data
The most common use case for Data Feeds is to Get the Latest Price. However, AggregatorV3Interface also exposes functions which can be used to retrieve price data of a previous round ID.
There are two parameters that can cause Chainlink nodes to update:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Deviation Threshold | Chainlink nodes are monitoring prices of assets off-chain. The deviation of the real-world price of an asset beyond a certain interval triggers all the nodes to update. |
| Heartbeat Threshold | If the price stays within the deviation parameters, it will only trigger an update every X minutes / hours. |
You can find these parameters at data.chain.link on an example like ETH / USD.
To learn how data feeds update, see the Decentralized Data Model page.
Historical Rounds
As shown in the decentralized model, the consumer contracts call the proxy contract, which abstracts the underlying aggregator contract. The main advantage is to enable upgrades of the aggregator without impacting the consumer contracts. That also means that historical data can can be stored in different aggregators.
As show in the following sequence diagram, to get historical data, call the getRoundData function function and provide roundId as a parameter.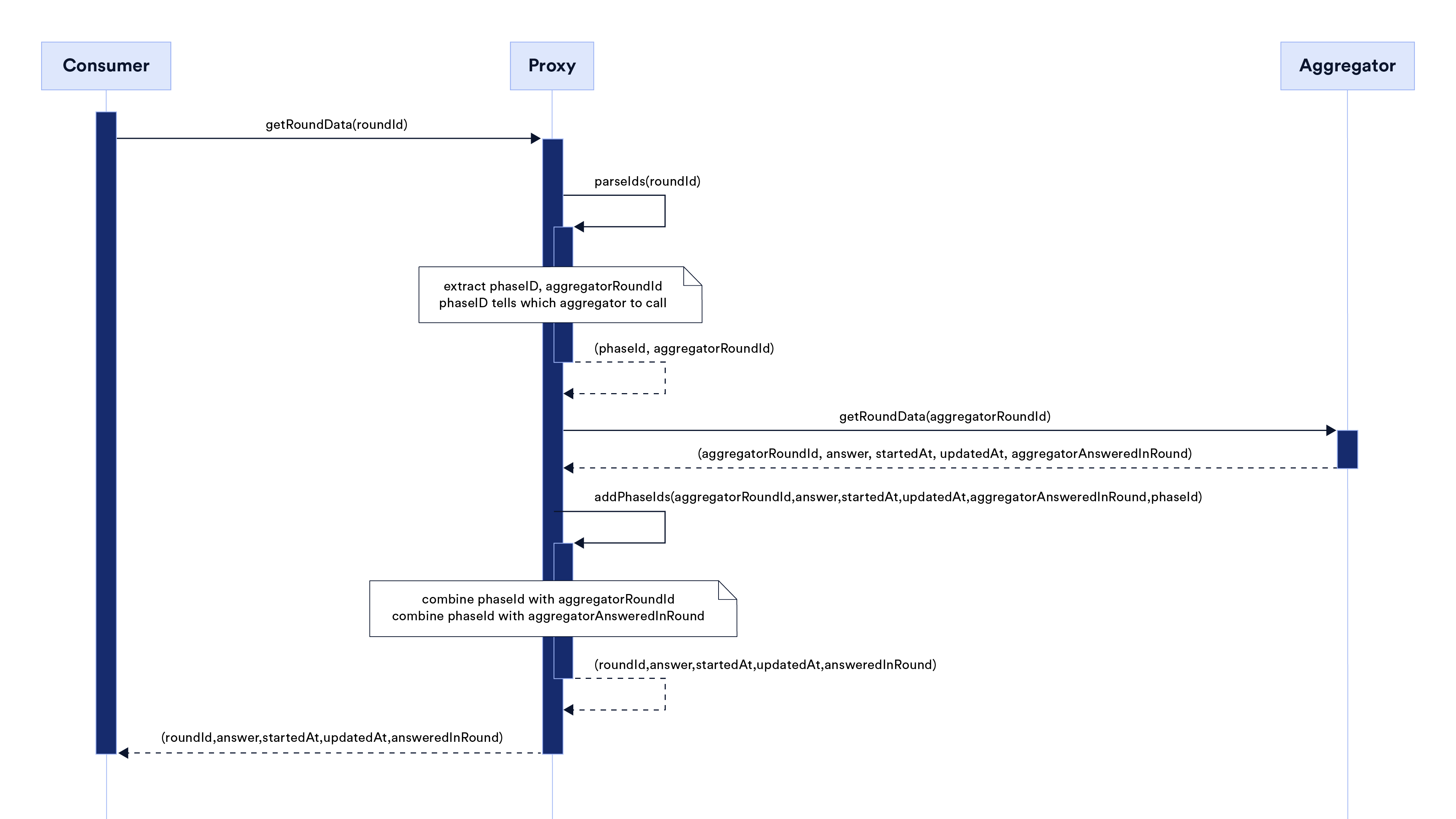
Note that roundIds have different meanings in proxy contracts and in aggregator contracts.
roundId in Aggregator (aggregatorRoundId)
Oracles provide periodic data updates to the aggregators. Data feeds are updated in rounds. Rounds are identified by their roundId, which increases with each new round. This increase may not be monotonic. Knowing the roundId of a previous round allows contracts to consume historical price data.
The examples in this document name the aggregator roundId as aggregatorRoundId to differentiate it from the proxy roundId.
roundId in Proxy
Because a proxy has references to current and all previous underlying aggregators, it needs a way to fetch data from the correct aggregator. The roundId is computed in the proxy contract as shown in the following example:
roundId = uint80((uint256(phaseId) << 64) | aggregatorRoundId);
where:
phaseIdis incremented each time the underlying aggregator implementation is updated. It is used as key to find the aggregator address.aggregatorRoundIdis the aggregatorroundId. The id starts at 1.roundIdis the computed round id. From the above formula, you can think of it as a large number containing thephaseIdand theaggregatorRoundId.
Note
The example formula above ensures that no matter how many times the underlying aggregator changes, the proxy roundId will always increase.
Example:
When you query historical data, it is important to know when you reach the end of the history of the underlying aggregator. As an example, if the latestRoundData function of the LINK / USD feed on Ethereum Mainnet returns roundId = 92233720368547771158, you can use this value to compute the phaseId and aggregatorRoundId:
phaseId = 92233720368547771158 >> 64: Right shifting an integer by 64 bits is equivalent to dividing it by 2^64:phaseId = 92233720368547771158/ 2^64 = 5. The current phase id is 5 , which means that this proxy has had 5 underlying aggregators since its initial deployment.aggregatorRoundId = uint64(92233720368547771158): This retrieves the first 64 bits from the right. To calculate this off-chain, you can use the following JavaScript example:
// First parse to BigInt to perform computation with big integers
const num = BigInt("92233720368547771158");
const num2 = BigInt("0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF"); // Largest 64bits integer
console.log(Number(num >> 64n)); // returns 5 (phaseId)
console.log(Number(num & num2)) // returns 13078 (aggregatorRoundId) . Use & (AND bitwise operator) which sets each bit to _1_ if both bits are _1_
Using 13078 as the current aggregator's round, get its historical data by looping over the getRoundData function:
- Start from the first round: 92233720368547758081 (result of 92233720368547771158 - 13078 + 1)
- Continue until the current round: 92233720368547771158
To get the historical data for previous aggregators, decrement the phaseId and start from round 1. For phase 4, get the starting roundId off-chain using the following JavaScript example:
const phaseId = BigInt("4");
const aggregatorRoundId = BigInt("1");
roundId = (phaseId << 64n) | aggregatorRoundId // returns 73786976294838206465n
Loop over the getRoundData function. Start at 73786976294838206465 and increment it until you get a revert. This means that you reached the last round for the underlying aggregator. The same process could be repeated for previous phaseIds (3,2,1).
Looping on-chain
The examples showed how to loop off-chain to fetch all historical data from a given proxy. You could also write a similar code on-chain, but be aware that this could cause very high gas prices if a state is changed within the same function.
getRoundData return values
The getRoundData function returns the following values:
roundId: The combination ofaggregatorRoundIdandphaseId(see explanation above). TheroundIdcan jump significantly when thephaseIdis updated.answeris the price.answeredInRound: The combination ofaggregatorAnsweredInRoundandphaseId.aggregatorAnsweredInRound: The round the answer was updated in. You can checkansweredInRoundagainst the currentroundId. IfansweredInRoundis less thanroundId, the answer is being carried over. IfansweredInRoundis equal toroundId, then the answer is fresh.startedAt: The timestamp when the round started.updatedAt: The timestamp when the answer was computed.
Important
A read can revert if the caller is requesting the details of a round that was invalid or has not yet been answered. If you are deriving a round ID without having observed it before, the round might not be complete. To check the round, validate that the timestamp on that round is not 0.
In a best-case scenario, rounds update chronologically. However, a round can time out if it doesn't reach consensus. Technically, that is a timed out round that carries over the answer from the previous round.
Solidity
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.7;
import "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/interfaces/AggregatorV3Interface.sol";
/**
* THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES HARDCODED VALUES FOR CLARITY.
* THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES UN-AUDITED CODE.
* DO NOT USE THIS CODE IN PRODUCTION.
*/
contract HistoricalPriceConsumerV3 {
AggregatorV3Interface internal priceFeed;
/**
* Network: Goerli
* Aggregator: ETH/USD
* Address: 0xD4a33860578De61DBAbDc8BFdb98FD742fA7028e
*/
constructor() {
priceFeed = AggregatorV3Interface(0xD4a33860578De61DBAbDc8BFdb98FD742fA7028e);
}
/**
* Returns historical price for a round id.
* roundId is NOT incremental. Not all roundIds are valid.
* You must know a valid roundId before consuming historical data.
*
* ROUNDID VALUES:
* InValid: 18446744073709562300
* Valid: 18446744073709554683
*
* @dev A timestamp with zero value means the round is not complete and should not be used.
*/
function getHistoricalPrice(uint80 roundId) public view returns (int256) {
(
uint80 id,
int price,
uint startedAt,
uint timeStamp,
uint80 answeredInRound
) = priceFeed.getRoundData(roundId);
require(timeStamp > 0, "Round not complete");
return price;
}
}
Javascript
/**
* THIS IS EXAMPLE CODE THAT USES HARDCODED VALUES FOR CLARITY.
* THIS IS EXAMPLE CODE THAT USES UN-AUDITED CODE.
* DO NOT USE THIS CODE IN PRODUCTION.
*/
const Web3 = require("web3") // for nodejs only
// Replace the provider URL with your own endpoint URL
const web3 = new Web3("https://rpc.ankr.com/eth_goerli")
const aggregatorV3InterfaceABI = [{ "inputs": [], "name": "decimals", "outputs": [{ "internalType": "uint8", "name": "", "type": "uint8" }], "stateMutability": "view", "type": "function" }, { "inputs": [], "name": "description", "outputs": [{ "internalType": "string", "name": "", "type": "string" }], "stateMutability": "view", "type": "function" }, { "inputs": [{ "internalType": "uint80", "name": "_roundId", "type": "uint80" }], "name": "getRoundData", "outputs": [{ "internalType": "uint80", "name": "roundId", "type": "uint80" }, { "internalType": "int256", "name": "answer", "type": "int256" }, { "internalType": "uint256", "name": "startedAt", "type": "uint256" }, { "internalType": "uint256", "name": "updatedAt", "type": "uint256" }, { "internalType": "uint80", "name": "answeredInRound", "type": "uint80" }], "stateMutability": "view", "type": "function" }, { "inputs": [], "name": "latestRoundData", "outputs": [{ "internalType": "uint80", "name": "roundId", "type": "uint80" }, { "internalType": "int256", "name": "answer", "type": "int256" }, { "internalType": "uint256", "name": "startedAt", "type": "uint256" }, { "internalType": "uint256", "name": "updatedAt", "type": "uint256" }, { "internalType": "uint80", "name": "answeredInRound", "type": "uint80" }], "stateMutability": "view", "type": "function" }, { "inputs": [], "name": "version", "outputs": [{ "internalType": "uint256", "name": "", "type": "uint256" }], "stateMutability": "view", "type": "function" }]
const addr = "0xA39434A63A52E749F02807ae27335515BA4b07F7"
const priceFeed = new web3.eth.Contract(aggregatorV3InterfaceABI, addr)
// Valid roundId must be known. They are NOT incremental.
let validId = BigInt("18446744073709554177")
priceFeed.methods.getRoundData(validId).call()
.then((historicalRoundData) => {
document.getElementById('get-price-field').value = historicalRoundData.answer
})
Python
# THIS IS EXAMPLE CODE THAT USES HARDCODED VALUES FOR CLARITY.
# THIS IS EXAMPLE CODE THAT USES UN-AUDITED CODE.
# DO NOT USE THIS CODE IN PRODUCTION.
from web3 import Web3
# Change this to use your own RPC URL
web3 = Web3(Web3.HTTPProvider('https://rpc.ankr.com/eth_goerli'))
# AggregatorV3Interface ABI
abi = '[{"inputs":[],"name":"decimals","outputs":[{"internalType":"uint8","name":"","type":"uint8"}],"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"inputs":[],"name":"description","outputs":[{"internalType":"string","name":"","type":"string"}],"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"inputs":[{"internalType":"uint80","name":"_roundId","type":"uint80"}],"name":"getRoundData","outputs":[{"internalType":"uint80","name":"roundId","type":"uint80"},{"internalType":"int256","name":"answer","type":"int256"},{"internalType":"uint256","name":"startedAt","type":"uint256"},{"internalType":"uint256","name":"updatedAt","type":"uint256"},{"internalType":"uint80","name":"answeredInRound","type":"uint80"}],"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"inputs":[],"name":"latestRoundData","outputs":[{"internalType":"uint80","name":"roundId","type":"uint80"},{"internalType":"int256","name":"answer","type":"int256"},{"internalType":"uint256","name":"startedAt","type":"uint256"},{"internalType":"uint256","name":"updatedAt","type":"uint256"},{"internalType":"uint80","name":"answeredInRound","type":"uint80"}],"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"inputs":[],"name":"version","outputs":[{"internalType":"uint256","name":"","type":"uint256"}],"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"}]'
# Price Feed address
addr = '0xA39434A63A52E749F02807ae27335515BA4b07F7'
# Set up contract instance
contract = web3.eth.contract(address=addr, abi=abi)
# Valid roundId must be known. They are NOT incremental.
# invalidRoundId = 18446744073709562300
validRoundId = 18446744073709554177
historicalData = contract.functions.getRoundData(validRoundId).call()
print(historicalData)